
Encryption protocols are essential VPN tools for encrypting your traffic. In 2025, it’s crucial to understand the ever-lasting WireGuard vs OpenVPN debate, as these are the most popular options. Some say OpenVPN is better, while others openly push WireGuard as the newer, superior protocol.
Regardless, you’ve seen these protocols in many providers. We’re talking about CyberGhost, Surfshark, PIA, Atlas VPN, and at least 20 more. But which protocol should you actually use? OpenVPN or WireGuard? And most importantly – how are they different?
Today’s article will take you on a stroll where we’ll discuss these protocols in-depth. We’ll explain each protocol, see which is better, and which one to use, and look at how these two stack against each other. Next time you’re choosing a protocol for your connection, you’ll know exactly which one to go for! Without further ado, let’s begin the WireGuard vs OpenVPN analysis.
What Is OpenVPN?
Let’s start with OpenVPN. If you’ve ever used a VPN, you know about this protocol. This is perhaps the most known, reliable, and tested protocol on the planet. On top of that, it’s not only a protocol found in VPNs but also a piece of software that you can install on desktop and mobile platforms.
OpenVPN was originally released for the first time in 2001. The man behind the project is James Yonan, who designed the protocol for safe and secure internet connections in Russia and Asia. Even today, James is the CEO of OpenVPN Inc., the same company that runs the protocol.
OpenVPN is, therefore, a tunneling protocol, which can transfer data using TCP or UDP. TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol, while UDP is User Datagram Protocol. Both are known for excellent security; TCP excels in reliability, and UDP generally provides faster speeds.
Moreover, this protocol is known for excellent compatibility and easy implementation across a wide gamut of devices. By today’s standards, though, it’s slow, with long connection times. On the other hand, OpenVPN is suitable for getting over censorship, as it’s often combined with obfuscation.
This means VPNs with this protocol can sometimes be used in China. This, of course, depends on the level of encryption, obfuscation, and many other factors.
The takeaway is that this is an old, tried-and-tested protocol that you’ll find in 99% of the VPNs on the market.
What Is WireGuard?
In this WireGuard vs OpenVPN comparison, we also need to address the first protocol. This is a much more modern solution that emerged in 2019, with the first stable release. Depending on when you’re reading this article, the protocol is merely a few years “old.”
The man behind this protocol is Jason A. Donenfeld. He wanted something much faster, more secure, and definitely more reliable than “traditional” protocols, most notably OpenVPN and IKEv2. Much like its rival, it also uses UDP for data transfer but TCP isn’t supported.
However, the protocol is known for extremely fast speeds, shorter connection times, and better performance. This is because it’s lightweight, it’s made with fewer lines of code, and designed to work with modern processors that can take full advantage of it.
It’s vital to mention that both WireGuard and OpenVPN are open-source protocols. Since WireGuard is newer, it’s more prone to changes, improvements, and implementation in next-gen VPN technology. For example, NordVPN took this protocol and made NordLynx, an improved version of it.
Because of its numerous benefits that we’ll discuss, providers were quick to implement it as well. Today, even free VPNs are fast thanks to this protocol that brought substantial performance boosts. But is WireGuard better than OpenVPN? Is it truly THAT good? Let’s see…
WireGuard vs OpenVPN: Which One Is Better?
Since we now know what are WireGuard and OpenVPN protocols, we need to compare them side by side. This will give us a clearer image of which one is better across several tests. Without further ado, our tests are below. They’re pretty interesting, so scroll down and take a look at them.
OpenVPN vs WireGuard Speed Test
It’s evident, according to many tests we did, that WireGuard is faster than OpenVPN. This can be seen even during the connection process. For example, when you’re connecting to a server with OpenVPN, you’ll notice that you’ll have to wait for 3-5 seconds for it to be complete.
On the other hand, WireGuard has pretty much instant connections and you’ll wait for a second or two. To further prove this claim, we decided to test both providers for speeds in our OpenVPN vs WireGuard comparison. For this one, we used “vanilla” WireGuard from CyberGhost.
Our tests were done on 3 separate VPN locations but first, let’s check our native internet speeds:
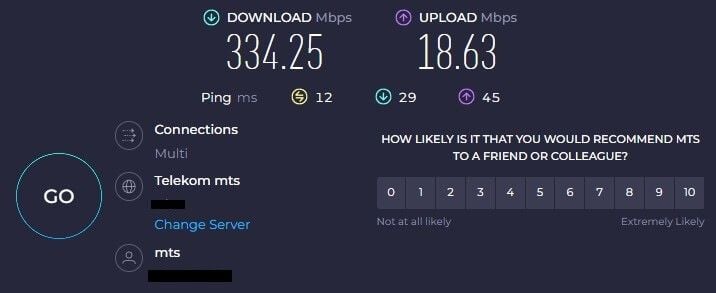
With this result in place, we went ahead and tested CyberGhost on the UK, the US, and Japanese servers using WireGuard (left) and then OpenVPN (right). The respective results are below:
UK:

US:
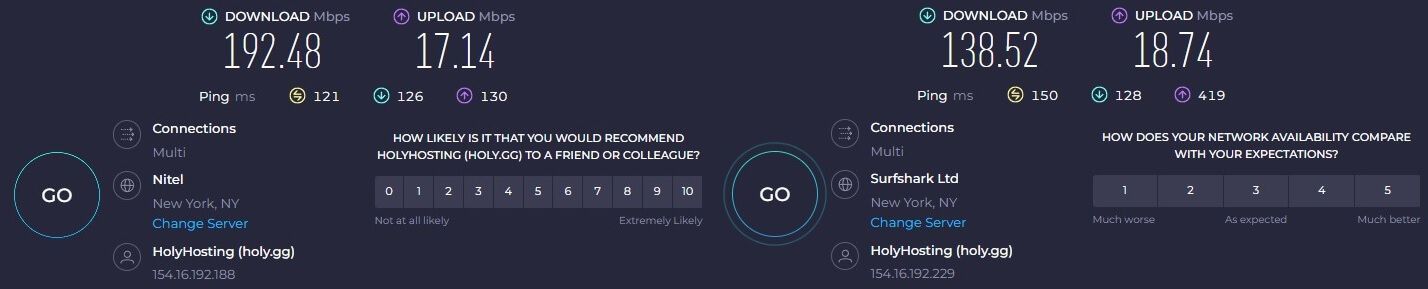
Japan:
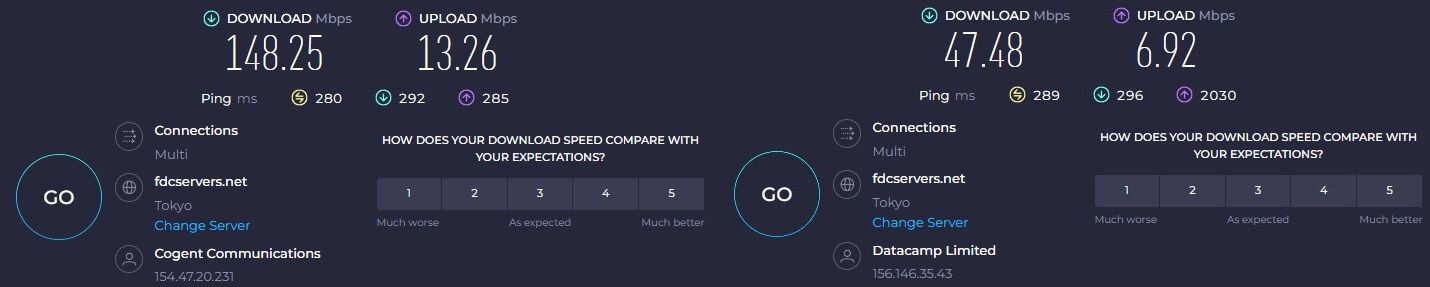
As you can see, WireGuard shows faster speeds, more or less noticeable on some servers. However, you can also notice that latency is lower as well, with better overall upload/download speeds across the board. The difference, as you can see, can go up to 100 or more percent (the Japanese server)!
This is still a significant difference and one worth taking into account when selecting between the two protocols. By the way, for a full test of this provider, visit our CyberGhost review to find out more. In short, WireGuard WINS the first duel.
Security & Privacy
Security and privacy are extremely important for these cutting-edge tunneling protocols. Some speculations were that WireGuard isn’t “private” compared to OpenVPN but that isn’t the case in 2025. For example, both protocols support customizable encryption options.
Lower encryption means faster speeds and vice versa. At the time of writing this WireGuard vs OpenVPN duel, we’re talking about five encryption ciphers to pick from. These include:
- AES-128-CBC, AES-128-GCM,
- AES-192 CBC, AES-256-CBC,
- and AES-256-GCM (the strongest one).
The difference, here, is in the type of supported encryption. The newer protocol relies on ChaCha20 encryption with Poly1305 authentication. Both are extremely safe and secure. The older protocol relies on ChaCha20, AES, Camellia, and Blowfish encryption types.
Authentication is the same – Poly 1305. As you can see they can be pretty much the same, supporting several types of encryption and authentication. OpenVPN is more customizable, while its newer rival is limited to the aforementioned parameters.
Privacy-wise, they’re both exquisite. Ultimately, it boils down to the provider and its logging practices and not encryption protocols. WireGuard was known for storing IPs on the server, which was fixed later on. Keep in mind that even poorly-configured OpenVPN can suffer from the same problem.
Thus, in terms of privacy, they’re neck and neck. In the end, this WireGuard vs OpenVPN comparison is a DRAW.
Circumventing Censorship
Getting over censorship is another vital OpenVPN vs WireGuard comparison. In short, the newer protocol sucks here, as it supports only UDP. UDP is faster, as said, which explains why the protocol provides better performance in the first place.
Unfortunately, TCP, while less reliable, is, at the same time, more suitable for getting over DPI and censorship in general. It’s not strange that obfuscated servers in NordVPN use OpenVPN TCP and work extremely well, at the cost of slight speed reduction.
We tested the newer protocol many times thanks to our colleagues from China, Russia, and Turkey. They, also reported that using OpenVPN produced almost no problems. Whereas, at times of severe VPN crackdowns in the respective countries, WireGuard seemed to struggle a lot.
That said, OpenVPN comes out on top in this test against WireGuard.
Compatibility
While VPNs work on all devices, not all devices support both protocols. Also, not all VPN providers have WireGuard on mobile apps. You’ll find that some free VPNs for iPhones lack this protocol, for example. On the other side, OpenVPN is supported on almost all platforms and VPN apps.
In 2025, we must notice an increasing trend of using WireGuard even on mobile devices. ExpressVPN, CyberGhost, NordVPN, Surfshark, PIA, and many others already have this protocol on iOS and Android apps. What’s more, it increasingly becomes a default protocol in many popular VPNs!
One thing to note is that WireGuard usually isn’t supported by routers – only a few providers offer this feature (most notably, Mullvad). As such, if you’re looking to set up a VPN on a router, know that you’ll most likely be limited to OpenVPN or an outdated protocol like PPTP or SSTP.
As we speak, OpenVPN is a slight WINNER in terms of compatibility. However, with its rival quickly catching up, we don’t see this being true for years to come. We’ll have to wait and see.
Data Usage
It’s known that using a VPN leads to increased data consumption. There’s encryption and tunneling, both of which require more data due to sending and receiving additional information through the internet. This OpenVPN vs WireGuard comparison will tell you which one is more data-friendly.
Let’s start with mobile users – the most affected ones. Consuming more data is detrimental to mobile users who frequently rely on their mobile data. If this data is limited, using a VPN will make it dwindle even faster. If you’re in this situation, which protocol will be a better option?
In short, WireGuard consumes less data than OpenVPN. The difference isn’t negligible, however, as we’re talking about a 5% or so data increase with this protocol. When using OpenVPN UDP or TCP, the increase in data usage goes up to nearly 20%.
So, instead of spending, let’s say, 600 MB in a particular session, you’ll spend 630 MB with WireGuard and 720 MB with OpenVPN. If we multiply everything by 10 or 100, the difference is stark. After all, the newer protocol is far less complex than the older OpenVPN, which also plays a role.
For now, the data usage round is WON by WireGuard.
Complexity
While we’re at complexity, let’s talk about one of WireGuard’s aces. We’ve already learned that OpenVPN is more resource-taxing, so it consumes more data, and by extension, uses more battery power. After all, it’s a more complex protocol, with around 70,000 lines of code.
In comparison, WireGuard has only 4,000 or so lines of code, making it incredibly simple. Since both protocols are open-source, the latter is at a huge advantage. First, it’s easier to improve upon and maintain, as the administrator has to go through fewer lines of code.
OpenVPN and its 70,000 lines of code require more than a few experts to carefully examine the code and fix potential problems or apply updates. More importantly, it’s much easier to audit and verify WireGuard than OpenVPN – yet another MAJOR advantage.
Since both of them now have official audits, this isn’t something worth bothering with. Still, any new improvements over the newer protocol’s formula will be simpler to verify and audit in the future, and that makes WireGuard the WINNER of this comparison.
WireGuard vs OpenVPN: The Final Verdict
After numerous tests we conducted, you can see that WireGuard wins with a score of 4:3. While at first, the difference between the two seems colossal, both protocols are safe, secure, and reliable. WireGuard’s advantages lie in faster speeds, shorter connection times, ease of use, and lower data usage.
OpenVPN’s advantages include better device compatibility, which will most likely change soon, as well as the TCP option for bypassing censorship. Now, the final question is – which protocol to use, WireGuard or OpenVPN? Our answer is BOTH.
In the end, it boils down to your needs. To summarize our thoughts, we’ll say that:
- You should use WireGuard for better performance, lower data consumption, smaller battery drain on mobile devices, and playing games with a VPN.
- Or, if you want to get over censorship, use a VPN on a router, if you’re wary of new technologies and you don’t want to test out new things, use OpenVPN.
That’s it. You now know what both protocols are, how they stack against each other, and when/why to use them. It’s relevant to say that OpenVPN, despite being slightly outdated, isn’t BAD by any means. It’s just overshadowed by higher demands for faster speeds and stable performance.
FAQ
To put things into perspective, let’s briefly answer a few more relevant questions related to the subject matter.
Which VPNs offer WireGuard?
OpenVPN is a protocol you’ll find in every provider, except for a selected few. However, WireGuard is a bit harder to find, although, again, this WILL change soon, with the inclusion of this protocol even in free providers. The best providers that include this protocol include:
- CyberGhost
- NordVPN
- Surfshark
- Private Internet Access
- ProtonVPN
- Atlas VPN, and many others…
NordVPN’s version is the best here. It’s the NordLynx protocol that improves upon the basic formula of this protocol, with stronger security, more privacy, and even faster speeds. The rest of the pack offers “vanilla” WireGuard, which, while inferior, is still superb.
Will OpenVPN disappear in the future?
No – at least it’s highly unlikely. WireGuard can’t fully replace OpenVPN, and as you learned, this protocol is indeed better in many scenarios. Simply put, OpenVPN can’t be replaced completely, especially when talking about censorship circumvention and TCP support.
Is WireGuard the fastest protocol?
It is one of the fastest but not #1, definitely. NordLynx is faster, and so is Lightway, a protocol from ExpressVPN that exhibits the best performance overall. We’ll also take into account some TLS-encrypted protocols that also seem to be fast – Hydra in Hotspot Shield, for instance.
However, TLS is a basic form of encryption, so the overall security suffers. If we were to rank the top 3 protocols by speed, it’d be Lightway, NordLynx, and then WireGuard.